背景
Apache POI是用Java编写的免费开源的跨平台的 Java API,Apache POI提供API给Java程序对Microsoft Office格式档案读和写的功能。POI为“Poor Obfuscation Implementation”的首字母缩写,意为“简洁版的模糊实现”。
问题描述
最近在使用Apache POI操作word的时候,发现word文档的画布这个对象很难对其进行一些操作,例如将这个画布复制到另外一个文档、操作画布内的形状或文本。
如下图,在示例word文档表格中存在一个“画布”对象
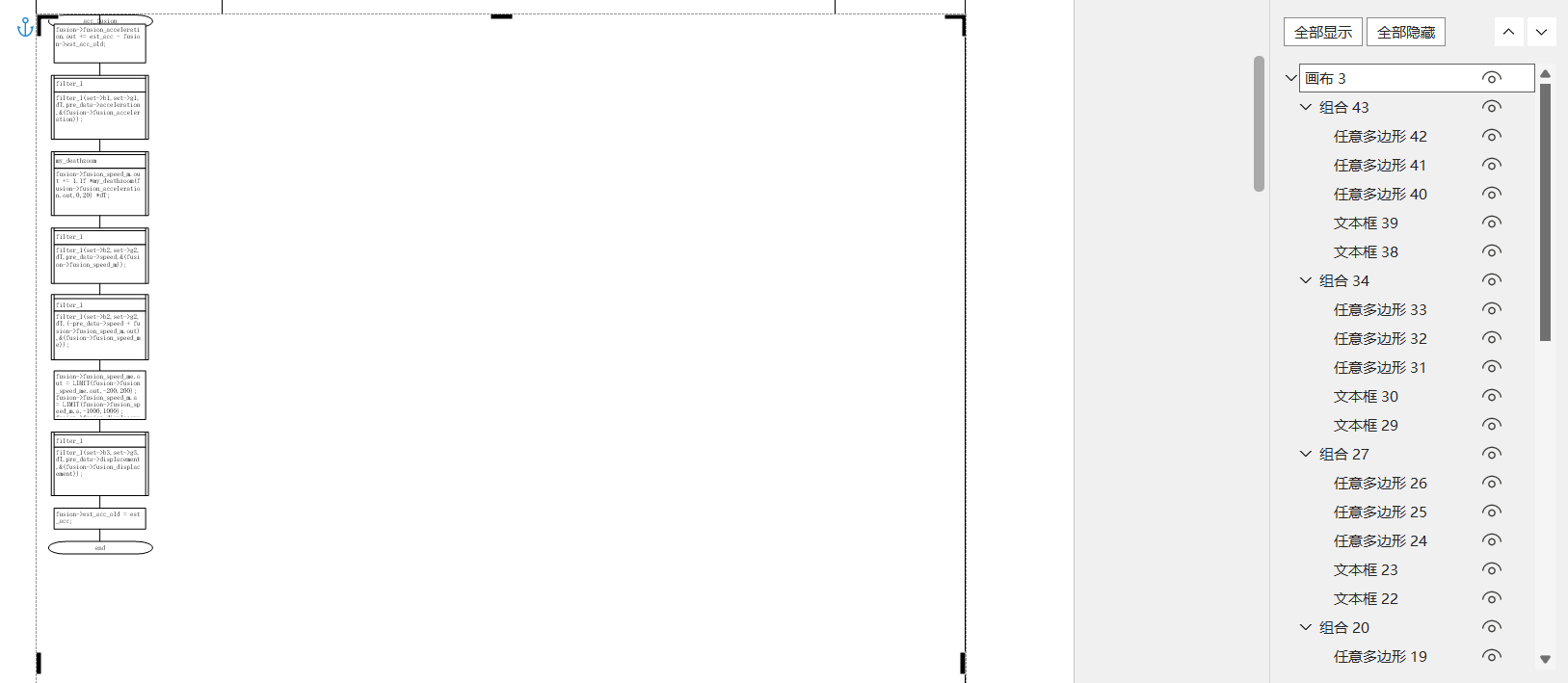
使用如下代码:
// 导入word文档
inputStream = new FileInputStream("path/exampleFile");
doc = new XWPFDocument(inputStream);
// 获取文档中所有表格
List<XWPFTable> tables = doc.getTables();
for (XWPFTable table : tables) {
// 定位画布对象所处的单元格
XWPFTableCell cell = table.getRow(2).getCell(0);
try {
for (XWPFParagraph paragraph : cell.getParagraphs()) {
// 处理每个画布对象
// ……
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("未知错误!");
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}debug模式下运行,观察“画布”对象:
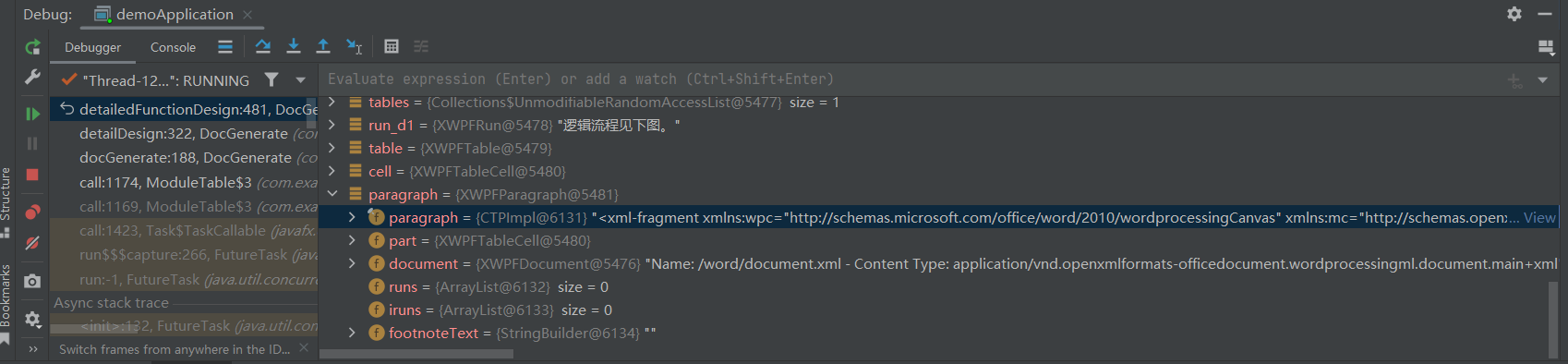
可以看到画布对象被poi解析为一个XWPFParagraph对象,这是一个很笼统的对象,官方所提供的api也非常有限,所以利用这个对象是不好操作的,但是这个对象有一个final修饰的成员变量paragraph,类型为CTP
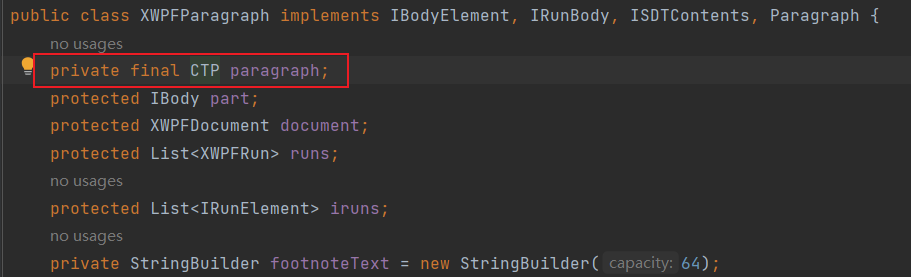
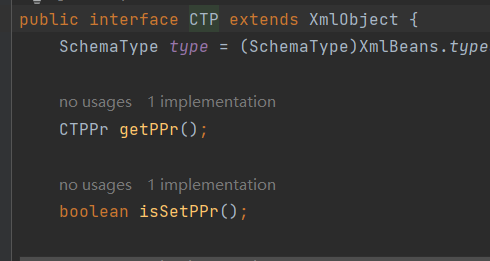
所以CTP是一个接口,实现类是CTPImpl类,而且这个类是继承XmlObject,那么就很容易想到使用XML。
XML是什么?
XML(可扩展标记语言)是一种用于标记文档和数据的语言,它可以帮助用户定义文档的结构和内容。在word中,XML架构被用来定义文档的内容元素、属性和其结构关系。通过使用XML架构,用户可以轻松地创建和编辑文档,同时也可以方便地对文档进行数据的导入和导出。
简单来说,在Microsoft Word中,用户可以通过XML来定义和处理文档的内容。那么操作XML不就等于在操作Word?
事实上,我们将一个word后缀由.docx改为.zip后,再进行解压,可以得到这些文件

解释,主要关注“word”文件夹:
| _rels | .rels的文件是一个页面布局文件。 rels就是Relationships(关系)的缩写。 通常rels文件不显示在最终版本中,但如果你看到它们出现在解压后目录里,那是因为Word需要这些来保持你的章节、图片链接等元素之间的连接。 |
| docProps | 文档属性文件。存放文档的元数据。 |
| word | 实际存放word中XML元素的文件,并显示在最终的版本中。 |
| [Content_Types].xml | 定义content_type。 |
示例XML:
与HTML类似,以封闭标签表示元素
<w:pict>表示word画布对象
以<v:>开头的标签是与画布相关的:<v:group>表示word组合对象;<v:shape>表示word形状;<v:textbox>表示word文本框
<xml-fragment xmlns:wpc="http://schemas.microsoft.com/office/word/2010/wordprocessingCanvas" xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006" xmlns:o="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:office:office" xmlns:r="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/officeDocument/2006/relationships" xmlns:m="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/officeDocument/2006/math" xmlns:v="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:vml" xmlns:wp14="http://schemas.microsoft.com/office/word/2010/wordprocessingDrawing" xmlns:wp="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/drawingml/2006/wordprocessingDrawing" xmlns:w="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/wordprocessingml/2006/main" xmlns:w14="http://schemas.microsoft.com/office/word/2010/wordml" xmlns:w10="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:office:word" xmlns:w15="http://schemas.microsoft.com/office/word/2012/wordml" xmlns:wpg="http://schemas.microsoft.com/office/word/2010/wordprocessingGroup" xmlns:wpi="http://schemas.microsoft.com/office/word/2010/wordprocessingInk" xmlns:wne="http://schemas.microsoft.com/office/word/2006/wordml" xmlns:wps="http://schemas.microsoft.com/office/word/2010/wordprocessingShape" xmlns:wpsCustomData="http://www.wps.cn/officeDocument/2013/wpsCustomData">
<w:pPr>
<w:pStyle w:val="7"/>
<w:jc w:val="left"/>
</w:pPr>
<w:r>
<w:rPr>
<w:lang w:eastAsia="zh-CN"/>
</w:rPr>
<w:pict>
<v:group id="_x0000_s1085" o:spid="_x0000_s1085" o:spt="203" style="position:absolute;left:0pt;margin-left:-2.85pt;margin-top:-1.4pt;height:672.75pt;width:481.9pt;z-index:251659264;mso-width-relative:page;mso-height-relative:page;" coordorigin="-57,-28" coordsize="9638,13455" editas="canvas">
<o:lock v:ext="edit"/>
<v:shape id="_x0000_s1084" o:spid="_x0000_s1084" o:spt="75" type="#_x0000_t75" style="position:absolute;left:-57;top:-28;height:13455;width:9638;" filled="f" o:preferrelative="f" stroked="f" coordsize="21600,21600">
<v:fill on="f" focussize="0,0"/>
<v:stroke on="f" weight="0pt" joinstyle="miter"/>
<v:imagedata o:title=""/>
<o:lock v:ext="edit" text="t" aspectratio="t"/>
</v:shape>
<v:shape id="_x0000_s1086" o:spid="_x0000_s1086" o:spt="110" type="#_x0000_t110" style="position:absolute;left:1029;top:1135;height:1224;width:3211;" coordsize="21600,21600">
<v:path/>
<v:fill focussize="0,0"/>
<v:stroke joinstyle="miter"/>
<v:imagedata o:title=""/>
<o:lock v:ext="edit"/>
<v:textbox inset="0.381mm,0.381mm,0.381mm,0.381mm">
<w:txbxContent>
<w:p>
<w:pPr>
<w:pStyle w:val="23"/>
</w:pPr>
<w:r>
<w:t>for(msgCount = 0; msgCount < stBusInitMsg.ucMsgNum; msgCount++)</w:t>
</w:r>
</w:p>
</w:txbxContent>
</v:textbox>
</v:shape>
<v:shape id="_x0000_s1087" o:spid="_x0000_s1087" o:spt="202" type="#_x0000_t202" style="position:absolute;left:4240;top:1538;height:194;width:420;mso-wrap-style:none;" filled="f" stroked="f" coordsize="21600,21600">
<v:path/>
<v:fill on="f" focussize="0,0"/>
<v:stroke on="f" joinstyle="miter"/>
<v:imagedata o:title=""/>
<o:lock v:ext="edit"/>
<v:textbox inset="0.381mm,0.381mm,0.381mm,0.381mm" style="mso-fit-shape-to-text:t;">
<w:txbxContent>
<w:p>
<w:pPr>
<w:pStyle w:val="19"/>
</w:pPr>
<w:r>
<w:t>FALSE</w:t>
</w:r>
</w:p>
</w:txbxContent>
</v:textbox>
</v:shape>
<!--此处省略大量shape标签-->
</v:group>
</w:pict>
</w:r>
</xml-fragment>前置工作:Java实现样式复制
为了能够确保接下来的操作在两个文档之间顺利进行,首先将源文档的样式布局复制到目标文档中。
- 获取源文档的所有样式,保证复制后样式不变
XWPFStyles styles = doc.getStyles();- 复制源文档样式
/**
* 复制文档布局
*
* @param srcDoc 源文档
* @param destDoc 目标文档
*/
public static void copyLayout(XWPFDocument srcDoc, XWPFDocument destDoc) {
String[] styleNames = {
"GAIO_PageFont",
"GAIO_FlowLabel",
"GAIO_FlowCaseLabel",
"GAIO_FlowCode",
"GAIO_FlowComment",
"GAIO_FlowText",
"GAIO_FootCenter",
"GAIO_FootLeft",
"GAIO_FootRight",
"GAIO_HeaderCenter",
"GAIO_HeaderLeft",
"GAIO_HeaderRight"
};
for (String styleName : styleNames) {
XWPFStyle style = srcDoc.getStyles().getStyleWithName(styleName);
copyStyle(srcDoc, destDoc, style);
}
}
/**
* 复制指定样式
*
* @param srcDoc 源文档
* @param destDoc 目标文档
* @param style 目标样式
*/
public static void copyStyle(XWPFDocument srcDoc, XWPFDocument destDoc, XWPFStyle style) {
if (destDoc == null || style == null) {
return;
}
if (destDoc.getStyles() == null) {
destDoc.createStyles();
}
destDoc.getStyles().addStyle(style);
}Java最终实现
这里以处理word中的画布为例,裁剪画布大小,使画布中的所有元素保持原有样式并居中
获取插入位置的光标:
/**
* 获取插入位置
*
* @param doc 文档对象
* @param targetText 查找文本
* @return 光标
*/
public static XmlCursor getInsertPos(XWPFDocument doc, String targetText) {
for (XWPFParagraph paragraph : doc.getParagraphs()) {
if (paragraph.getText().contains(targetText)) {
//BigInteger numID = paragraph.getNumID();
XmlCursor cursor = paragraph.getCTP().newCursor();
cursor.toEndToken();
if (cursor.toNextToken() == XmlCursor.TokenType.START) {
return cursor;
}
}
}
return null;
}处理源文档中的画布对象,并将其插入光标位置:
/**
* 处理画布
* 纵向裁剪画布+居中
*
* @param doc 文档对象
* @param paragraph 画布对象
* @param docCursor 文档指针
* @throws Exception 异常在方法外捕获写入日志
*/
public static void flowchartProcessing(XWPFDocument doc, XWPFParagraph paragraph, XmlCursor docCursor) throws Exception {
String paragraphXMLStr = paragraph.getCTP().toString();
// 获取距离父级顶部最高位置的shape参数
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("<v:shape[^>]*top:(-?\\d+)[^>]*height:(-?\\d+)[^>]*>");
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(paragraphXMLStr);
int top = 0;
int height = 0;
int index = 0;//不匹配第一个shape标签
while (matcher.find()) {
index++;
// 获取当前匹配到的top和height
int cur_top = Integer.parseInt(matcher.group(1));
int cur_height = Integer.parseInt(matcher.group(2));
if (top <= cur_top && index != 1) {
// 更新top和height
top = cur_top;
height = cur_height;
}
}
// 获取left最大值
int left = 0;
DocumentBuilder db = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance().newDocumentBuilder();
InputSource is = new InputSource(new StringReader(paragraphXMLStr));
org.w3c.dom.Document xmlDoc = db.parse(is);// 解析VML
NodeList shapes = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("v:shape");// 获取<v:shape>标签
NodeList groups = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("v:group");// 获取<v:group>标签
NodeList lines = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("v:line");// 获取<v:line>标签
// 遍历<v:shape>标签
for (int i = 0; i < shapes.getLength(); i++) {
Element shape = (Element) shapes.item(i);
// 检查标签是否在<v:group>内部(除去最外层<v:group>)
if (shape.getParentNode().getNodeName().equals("v:group") && !((Element) shape.getParentNode()).hasAttribute("editas")) {
continue;
}
// 获取left属性值
String style = shape.getAttribute("style");
int cur_left = Integer.parseInt(style.split("left:")[1].split(";")[0]);
left = Math.max(cur_left, left);// 更新left
}
// 遍历<v:group>标签
for (int i = 0; i < groups.getLength(); i++) {
Element group = (Element) groups.item(i);
// 检查<v:group>是否是最外层标签
if (group.hasAttribute("editas")) {
continue;
}
// 获取left属性值
String style = group.getAttribute("style");
int cur_left = Integer.parseInt(style.split("left:")[1].split(";")[0]);
left = Math.max(cur_left, left);// 更新left
}
if (left < 7000) {
// 平移量
int translate_x = (8200 - left) / 2;
// 修改left
// 修改<v:shape>标签,第一个不修改
for (int i = 1; i < shapes.getLength(); i++) {
Element shape = (Element) shapes.item(i);
// 检查标签是否在<v:group>内部(除去最外层<v:group>)
if (shape.getParentNode().getNodeName().equals("v:group") && !((Element) shape.getParentNode()).hasAttribute("editas")) {
continue;
}
// 修改left属性值
String style = shape.getAttribute("style");
int cur_left = Integer.parseInt(style.split("left:")[1].split(";")[0]);
int new_left = cur_left + translate_x;
style = style.replace("left:" + cur_left, "left:" + new_left);
shape.setAttribute("style", style);
}
// 修改<v:group>标签
for (int i = 0; i < groups.getLength(); i++) {
Element group = (Element) groups.item(i);
// 检查<v:group>是否是最外层标签
if (group.hasAttribute("editas")) {
continue;
}
// 修改left属性值
String style = group.getAttribute("style");
int cur_left = Integer.parseInt(style.split("left:")[1].split(";")[0]);
int new_left = cur_left + translate_x;
style = style.replace("left:" + cur_left, "left:" + new_left);
group.setAttribute("style", style);
}
// 修改<v:line>标签
for (int i = 0; i < lines.getLength(); i++) {
Element line = (Element) lines.item(i);
// 检查标签是否在<v:group>内部(除去最外层<v:group>)
if (line.getParentNode().getNodeName().equals("v:group") && !((Element) line.getParentNode()).hasAttribute("editas")) {
continue;
}
// 检查标签是否存在from和to属性
if (line.hasAttribute("from") && line.hasAttribute("to")) {
// 获取from和to属性值
String from = line.getAttribute("from");
String to = line.getAttribute("to");
// 将from和to属性值的第一个参数加1000
int newFrom = Integer.parseInt(from.split(",")[0]) + translate_x;
int newTo = Integer.parseInt(to.split(",")[0]) + translate_x;
// 设置新的from和to属性值
line.setAttribute("from", newFrom + "," + from.split(",")[1]);
line.setAttribute("to", newTo + "," + to.split(",")[1]);
}
}
// 修改后的VML转为字符串
Transformer transformer = TransformerFactory.newInstance().newTransformer();
DOMSource source = new DOMSource(xmlDoc);
StringWriter writer = new StringWriter();
StreamResult result = new StreamResult(writer);
transformer.transform(source, result);// 将Document对象转换为字符串
paragraphXMLStr = writer.toString();// 获取转换后的字符串
}
// 解析VML
XmlObject xmlObject = XmlObject.Factory.parse(paragraphXMLStr);
XmlCursor cursor = xmlObject.newCursor();
boolean modify1 = false;// 修改group标签里面的coordsize
boolean modify2 = false;// 修改shape标签里面的coordsize
double newHeight = Math.round(((double) (top + height) / 550 / 0.035) * 10.0) / 10.0;// 计算新高度
int newcoordSize_y = 0;// 新y值
while (cursor.hasNextToken()) {
if (modify1 && modify2) {
break;
}
if (cursor.isStart()) {
if (cursor.getName().getLocalPart().equals("group")) {
// 修改高度
String style = cursor.getAttributeText(new QName("style"));
style = style.replaceFirst("height:(\\d+\\.?\\d*)pt", "height:" + newHeight + "pt");
// 修改比例
String coordSize = cursor.getAttributeText(new QName("coordsize"));
String[] coordSizeArr = coordSize.split(",");
newcoordSize_y = (height < 2000) ? (int) (Integer.parseInt(coordSizeArr[0]) / (481.9 / newHeight)) : (int) (Integer.parseInt(coordSizeArr[0]) / (481.9 / newHeight)) + 2000;
coordSizeArr[1] = String.valueOf(newcoordSize_y);
coordSize = String.join(",", coordSizeArr);
cursor.setAttributeText(new QName("style"), style);
cursor.setAttributeText(new QName("coordsize"), coordSize);
modify1 = true;
}
if (cursor.getName().getLocalPart().equals("shape")) {
// 修改比例
String style = cursor.getAttributeText(new QName("style"));
style = style.replaceFirst("height:(\\d+\\.?\\d*)", "height:" + newcoordSize_y);
cursor.setAttributeText(new QName("style"), style);
modify2 = true;
}
}
cursor.toNextToken();
}
String newXml = xmlObject.xmlText();
XWPFParagraph newParagraph = new XWPFParagraph(CTP.Factory.parse(newXml), doc);// 创建新流程图
XWPFTable flowchartTable = doc.insertNewTbl(docCursor);// 插入表格,占位置
flowchartTable.getCTTbl().getTblPr().unsetTblBorders();// 去掉表格边框
flowchartTable.getRow(0).setHeight((int) (((top + height) / 550 + 0.4) * 567));// 设置表格高度
XWPFTableCell flowchartCell = flowchartTable.getRow(0).getCell(0);
flowchartCell.getCTTc().addNewTcPr().addNewTcW().setW(BigInteger.valueOf(17 * 567));// 设置表格宽度
paragraph.setNumID(getNewNumberingId(doc, BigInteger.valueOf(1)));// 编号置空
flowchartCell.setParagraph(newParagraph);// 插入流程图
docCursor.toNextToken();
doc.insertNewParagraph(docCursor);
docCursor.toNextToken();
}算法流程分析
- 获取段落的 XML 字符串
- 获取元素距离父级顶部最高位置的
shape参数- 利用正则表达式匹配
<v:shape>标签中的top和height属性。 - 遍历匹配结果,更新
top和height的值,使其代表距离父级顶部最高位置的shape的相关参数。
- 利用正则表达式匹配
- 获取元素距离word左侧
left最大值- 借助
DocumentBuilder解析段落的 XML 字符串。 - 分别遍历
<v:shape>和<v:group>标签,获取left属性值,并更新left的最大值。
- 借助
- 平移元素使其居中
- 当
left小于 7000 时,计算平移量translate_x。 - 遍历
<v:shape>、<v:group>和<v:line>标签,修改其left属性值,实现元素的平移。 - 若
<v:line>标签存在from和to属性,则修改其第一个参数。 - 将修改后的 XML 文档转换为字符串。
- 当
- 解析 VML 并修改高度和比例
- 解析修改后的 XML 字符串。
- 遍历 XML 节点,修改
<group>和<shape>标签的height和coordsize属性。 - 获取修改后的 XML 字符串。
- 创建新流程图并插入新位置
- 依据修改后的 XML 字符串创建新的段落对象。
- 在文档中插入表格,设置表格的高度和宽度,并去除边框。
- 将新的段落插入到表格单元格中。
- 移动文档指针,插入新的段落。
实现效果
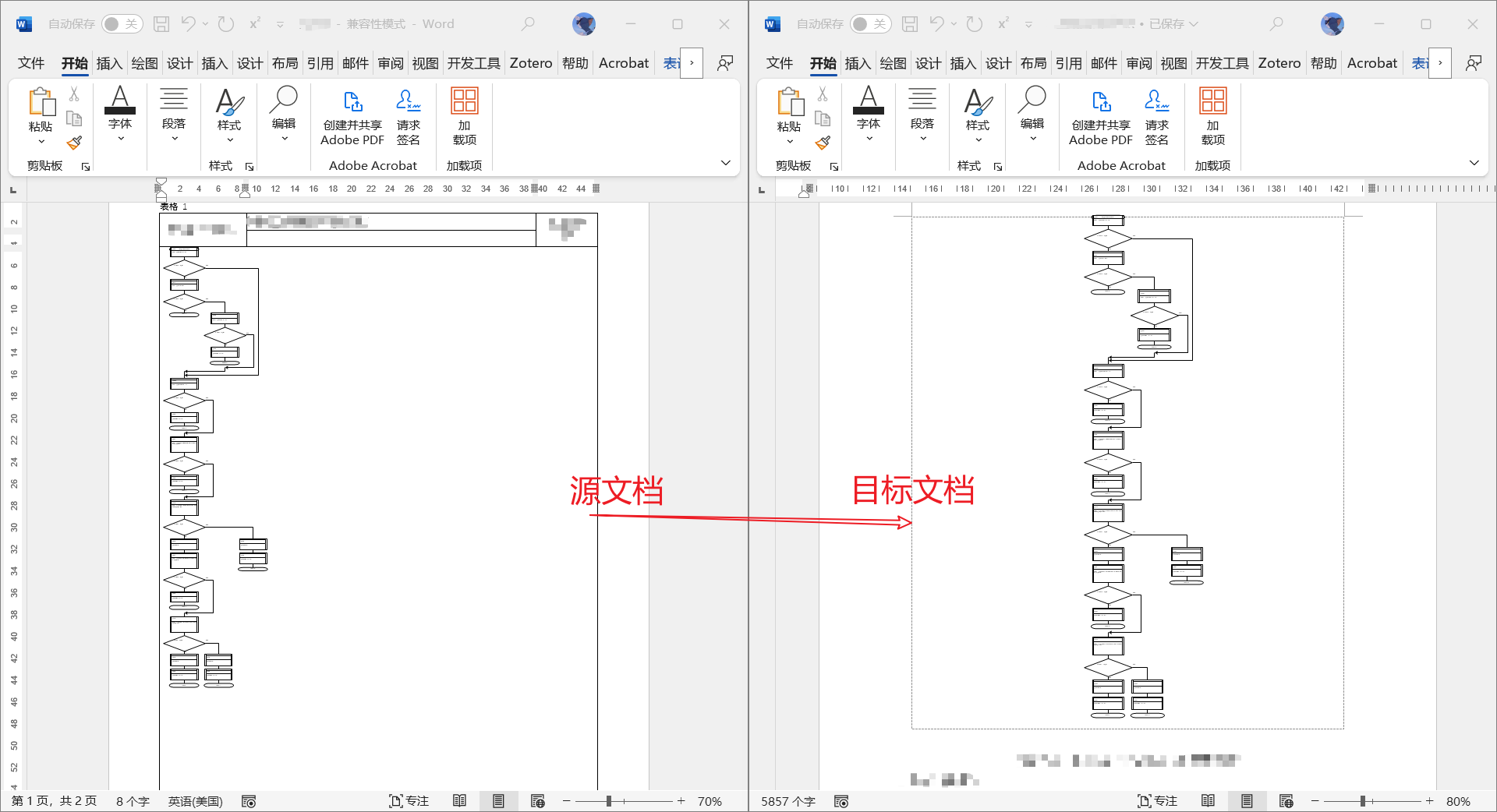
通过上述实现我们将源文档中画布对象复制到目标文档中,并将画布进行了裁剪,将流程图进行了居中。
注意
- 复制的样式名需要根据具体文档进行修改
- 平移量同样需要根据文档具体内容进行适配